Google Search Console is an essential part of every SEO toolbox, but how can you fix Google Search Console errors if you get an email from Google about errors from your website? Google search console helps monitor and correct errors on your website. Google Search Console allows you to analyze how your website is performing well.
It helps you understand the factors that help with the organic results. Google Search Console allows you to submit new content for crawling and indexing to improve your website visibility in the SERP.
Understanding Google’s Indexing Process in 2026:
For your website to show up on search engine results pages (SERPs), it must go through the following three processes:
Discovering:
It must first discover it before Google can crawl and index your site. The most common way to find a website is to process its XML sitemap. Google can also follow on and off-site links to discover websites and other methods.
Besides indexing errors, issues can arise during the discovery process as well. You can upload your XML sitemap to Google Search Console to ensure it discovers your site.
Crawling:
Once Google discovers the site, it’s in the queue for crawling. During a crawl, Googlebot will gather the metadata, title tags, alt tags, and more for indexing. Once the crawl is complete, it will request indexing.
Indexing:
This is the last phase of the process, where Googlebot attempts to make sense of the information from the crawling phase. In other words, the indexer will determine how relevant the content is for a search query.
As you can see, your website must pass the indexing phase to appear on search engines. Errors can occur during each phase, so it’s critical to familiarize yourself with Google search console error reports.
What are Search Console Errors?
One of the features of the Search Console is the ability to see any errors that your website is experiencing. These errors can range from issues with your website's structure to problems with your website's content.
Search Console errors are messages that tell you something is wrong with your website. These messages are divided into three categories:
- Indexing errors
- Crawl errors
- URL errors
Indexing errors are the most common type of error. These occur when Googlebot is unable to index your website's content. Crawl errors occur when Googlebot cannot crawl your website's pages, and URL errors happen when something is wrong with a specific URL.
Examples of Google Search Console Errors Notifications in 2026:
If the Google search console detects any new index coverage issue on your website, you will receive an email from Google. These errors can be fixed and resolved in the Google search console.
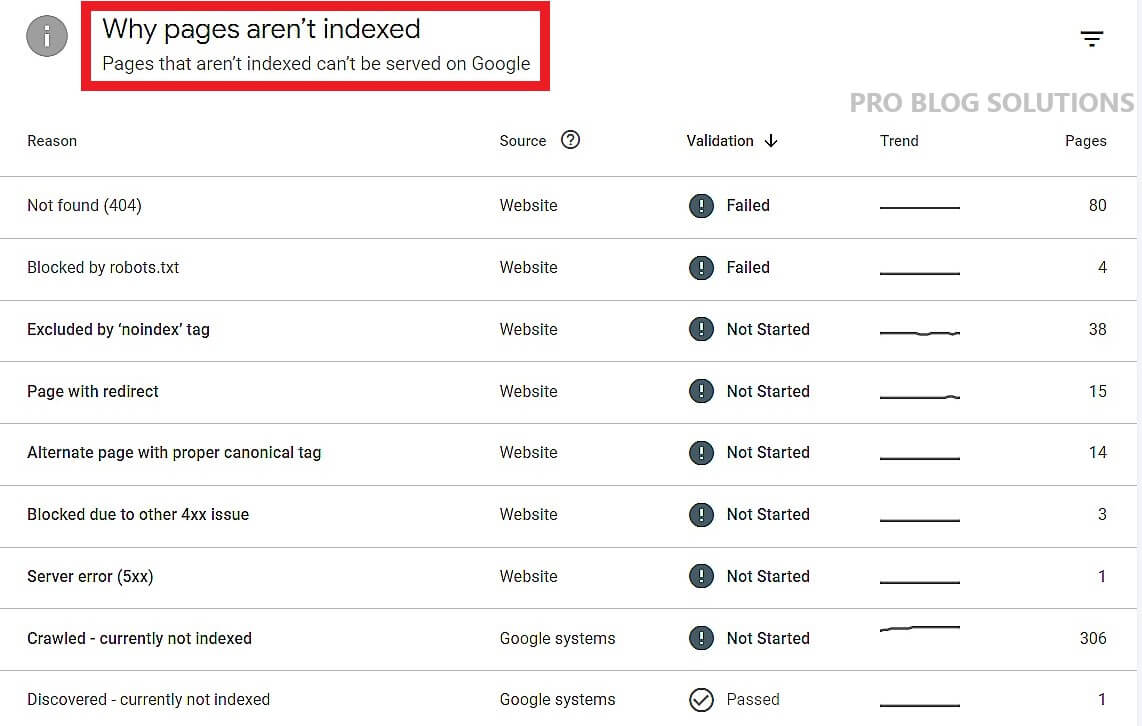
If you've logged into the Google search console recently, you most likely have seen some of these notifications:
- Submitted URL not found (404)
- Redirect error
- Submitted URL marked ‘noindex.’
- The submitted URL seems to be a Soft 404
- Server error (5xx)
- Soft 404 errors
- Text too small to read
- Clickable elements too close together
- Content wider than the screen
- The submitted URL has a crawl issue.
- Site not mobile-friendly
- Discovered – Currently Not Indexed
More related articles for you:
- Your Message to Gmail.Com Has Been Blocked Fix
- Install WhatsApp on PC and Fix Problems With Windows 11
- How to View – Mirror Phone Screen On PC?
- Best Tricks to Secure Your WordPress Website
- How to Improve Blog Audience?
Don't freak out when encountering issues in your Google Search Console account. Errors are common and anticipated in many situations.
Your first goal should be to resolve any CRAW ISSUES or NOT FOUND (404) issues, as these errors directly affect your rankings.
Why are Google Search Console Errors Important in 2026?
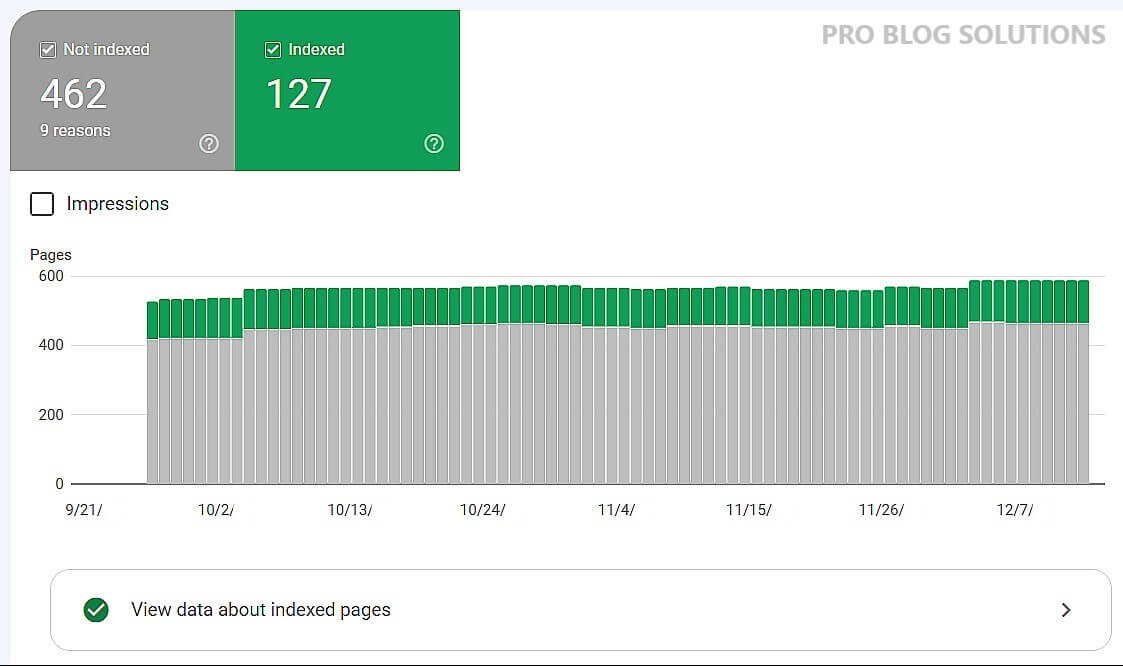
Google Search Console errors are essential for several reasons:
- Identification: These errors provide insights into potential issues that may hinder your website's performance on Google's search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Optimization: Resolving these errors can improve your website's visibility, ranking, and overall organic search traffic.
- User Experience: Fixing errors such as crawl errors and mobile usability issues ensures a seamless browsing experience for your audience.
- Site Health: Google Search Console errors help you identify and address technical issues like indexing errors and ensure your website functions correctly.
- Insights: Understanding these errors provides valuable information about how Google perceives your website and can guide your SEO strategies for better performance.
By paying attention to and resolving Google Search Console errors, website owners can enhance their online presence and deliver a better user experience to their audience.
Common Google Search Console errors can impede your website's performance and visibility on search engines. Crawl errors occur when search bots can't access certain pages, resulting in indexing issues. Mobile usability errors arise when pages aren't optimized for mobile devices, affecting user experience. Indexing errors occur when search engines have trouble understanding and categorizing your web pages.
1. Redirect Error
Redirect errors usually occur when a page has been redirected too many times or is redirecting to a 404 URL. These are pretty common when URLs have been changed multiple times.
It’s always a good idea to perform regular maintenance on your .htaccess file to ensure redirects are up-to-date and you aren’t redirecting to redirects and creating redirect chains. You can check your .htaccess file and redirect rules to sort these Google search console errors.
2. Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag
The alternate page with the proper canonical tag ‘error' means Google has spotted a duplicate of the page, but it is correctly canonicalized. Technically, this is not an error if you do not want this page to be indexed.
However, If you want the page indexed, more work is needed. First, remove the canonical tag and recrawl the URL with Google to see if this solves the issue. Sometimes, this will work well; other times, you are given another error, such as duplicate without user-selected canonical, which we will discuss next.
If your URL is not being indexed even after removing the canonical tag, you need to change the content on the page so Google no longer sees this as a duplicate. You can do this by adding or removing certain content, adding videos, or better matching the page to the search intent.
3. Submitted URL Not Found (404)
This is probably the most common coverage issue from Search Console. It means a page submitted to Google returns a 404 status code. This usually occurs when a page is deleted from a site but not from the sitemap.
Checking for errors in your Search Console should be a part of your SEO routine. Always optimize all your pages.
Fix Google Search Console Errors
Sitemap WordPress plugins such as Yoast will automatically delete them from the sitemap. Still, removing the page from the sitemap will have to be done manually for non-WordPress sites.
4. Submitted URL Excluded as Soft 404
If you're habitually using the URL inspection tool to speed up the indexing process for your pages, this notification may bother you.
The Googlebot will periodically crawl your website, looking for updates and new pages. For well-maintained websites, you can expect your pages to index in hours – for some websites, this could mean waiting days or weeks to index. But according to us, you don't need to worry too much if you get these Google search console errors.
5. Submitted URL Blocked By robots.txt
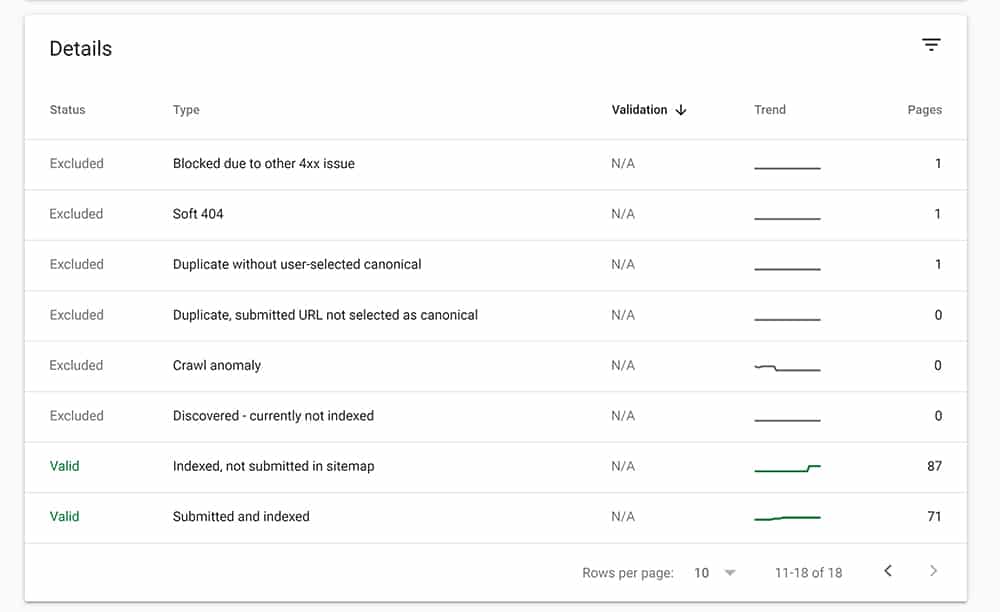
These URLs are blocked because of the site's robots.txt file and are not indexed by Google. This means Google has not found signals strong enough to warrant indexing these URLs. If they had, the URLs would be listed under “Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt.
6. Indexed, Though Blocked By robots.txt
The robots.txt file instructs Google's bot on which page to view and which should not be considered. When you have submitted a web page for indexing, it's blocked by the robots.txt file. This error means “Google has found your page and has instructions to ignore the robots file.
Use robots.txt tester to test and validate your robots.txt files.
7. URL Blocked Due to Other 4xx Issue
Sometimes, Googlebot is presented with a 4xx code, but it cannot reasonably determine what code it is. In this case, the URL blocked due to another 4xx issue is given to you. First, you must manually determine which code is being delivered by visiting the URL.
404 error: This means Googlebot has tried to crawl a URL that no longer exists.
400 error: The 400 error is thrown when a server cannot process the request, mainly due to a website being down for maintenance or if there is an error in the page's code.
403 error: This error is thrown when the website is restricted from being accessed. Is the website password-protected or protected behind a paywall?
Once you correctly identify which 4xx code is being thrown for each URL, you can fix each URL based on the correct code.
Implementing redirects or removing URLs from your website and sitemap if a 404 code has been thrown.
Find and fix any errors in your code if a 400 error has been thrown (if the website is not down for scheduled maintenance).
Remove any paywall functionality so Googlebot can crawl URLs with a 403 error.
8. Server Errors (5XX)
It means your server returned a 500-level error when the page was requested.
A 500 error means that something has gone wrong with a website’s server that prevented it from fulfilling your request. Something with your server prevented Google from loading the page in this case.
First, check the page in your browser and see if you can load it. If you can, there’s a good chance the issue has resolved itself, but you’ll want to confirm.
Email your hosting company and ask if the server has experienced any outages recently or if a configuration might be blocking Googlebot and other crawlers from accessing the site.
9. Alternative Page with Proper Canonical Tag
These URLs are duplicates of other URLs and are properly canonicalized to the preferred version of the URL. Action required: none.
10. Mobile Usability Errors
Websites should always be tailored for mobile devices, considering we live in a world increasingly turning to this type of web surfing. Mobile usability errors are common search console errors that will direct you to problems that pages have on a website that make it hard to navigate for users.
These issues, such as excessive text size, overlapping content, or slow loading times, can significantly hinder the user experience on mobile devices. Search engines prioritize mobile-friendliness, and websites with usability issues may experience lower rankings in mobile search results.
Content Wider Than Screen Error:
When content is wider than your screen, you usually have an element on your page or an image that hasn’t been appropriately sized for mobile devices. A common issue with WordPress sites is that this can happen if an image is given a caption or a plugin is used to generate an element that isn’t native to a theme.
A quick fix is immediately removing the image or element, causing the content to be wider than the screen. A long-term fix is to modify the code to ensure the content or element is responsive to mobile usability.
Viewport not Set Error:
Viewports or viewport properties inform browsers how to adjust a page’s dimensions. This then scales the page to the correct size of the screen. If a page does not define a viewport property, this can cause some issues.
The webpage may appear incorrectly on mobile devices, leading to a poor user experience. Search engines prioritize mobile-friendliness, and websites without a set viewport may experience penalties in mobile search rankings.
You can fix this by specifying the viewport using a meta viewport tag. Avoiding using wide, large elements on the site can prevent difficulties that require users to scroll horizontally. This simple yet effective measure can significantly improve mobile usability and enhance your website’s mobile-friendliness.
Small Text Errors:
This trait of mobile usability defines if the font size of a page is too small to be read and requires users to zoom in to consume content. To fix this error, specify a viewport in your pages and set font sizes to properly scale within the viewport. This can be done using relative units like em or rem rather than pixel value for font size.
Clickable Elements Too Close Error:
When a report says that clickable elements are too close together, this is usually due to elements like buttons and links being too close. This makes it hard for mobile users to click the elements they wish to access without tapping other elements they may not want.
Correct space and size elements are suitable for mobile users to ensure this doesn't happen. Google recommends 48 pixels and spacing between elements at least 8 pixels.
Adopt a mobile-first approach to website development and optimization. Use responsive design techniques, prioritize mobile page loading times, and test your website’s usability on various mobile devices.
11. Soft 404 Errors
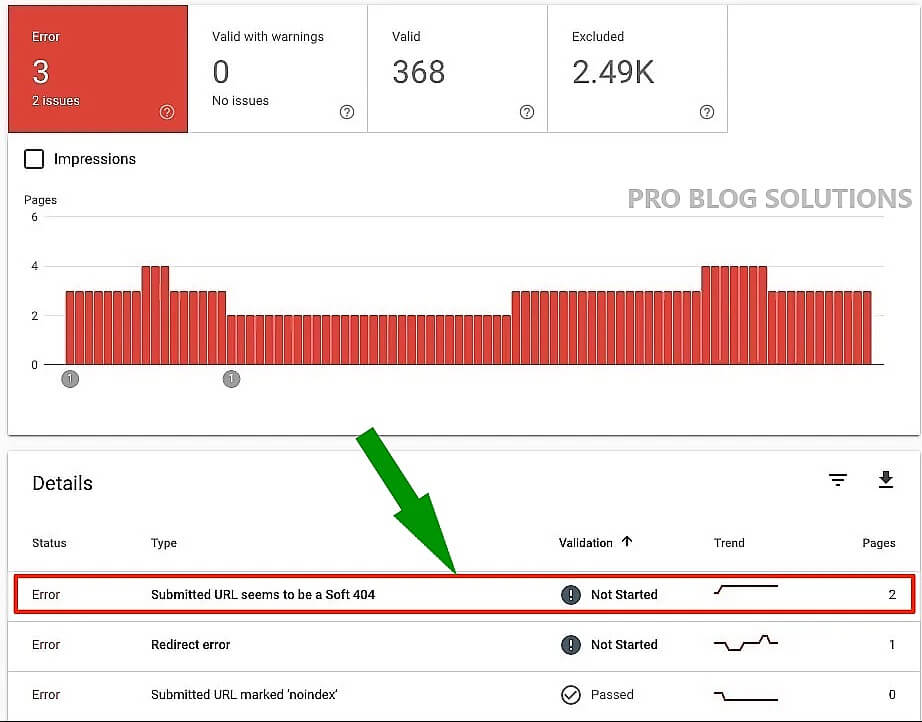
If your page is moved, replace it with the permanent 301 redirect, which is the proper way of redirecting your users. Use the URL inspection tool if it throws a soft 404 Error by mistake. Sometimes, the error is thrown because of the Thin and Duplicate content. Sometimes, it might be due to some technical glitch that leads to duplicate content issues.
12. Mobile Usability Issues
With Google's push towards mobile-first indexing, you want to ensure your website works well for smartphone users. Here's how to find mobile usability issues in Google Search Console:
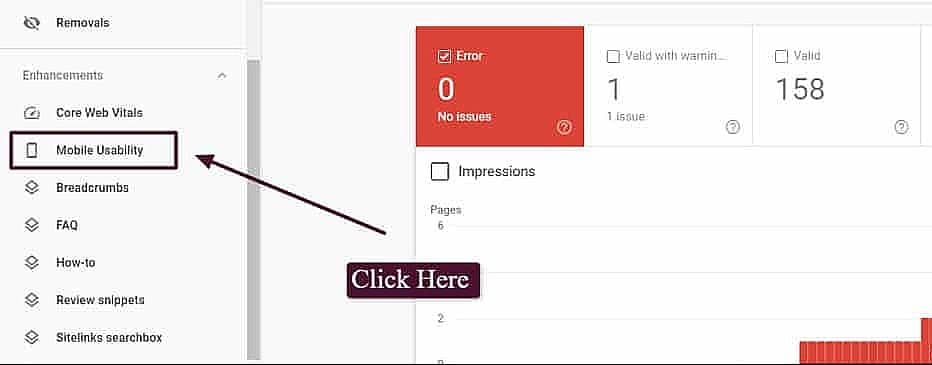
- Click “Mobile Usability” (under Enhancements).
- Make sure that “Error” is selected.
- If there are any errors, you can go to the Details box and learn which Errors are causing mobile issues.
- You can also double-click on any Error type to see the affected page URL.
13. Excluded by Noindex Tag
The “noindex” robots meta tag tells Google to “not index” this web page. Your page must be crawled and indexed by the Googlebot to appear in a Google search result. So if you have set a page to “noindex,” it will not appear in any Google searches.
How to Fix Excluded by Noindex Tag Error:
This problem involves changing the meta tag from “noindex” to “index.” How you do this will depend on your CMS.
In WordPress, you may have a Yoast plugin, which offers page-level and sitewide settings to noindex certain content types.
After removing the tag, resubmit the URL to Google through the URL inspection tool.
You may also like to read:
- 89 High DA DoFollow Article Submission Sites
- How to Get 50k Monthly Visitors to Your Blog?
- 207 High Domain Authority Backlink Sites
- How to Open WebP Images In Windows 10?
- How to Enable Mobile Data in Airplane Mode?
14. Discovered – Currently not Indexed

Cause: Google knows the page exists but was unable to crawl it.
Fixing this error: Make sure Googlebot can access your site, isn't bogged down by an excessive crawl delay (specified in your robots.txt file), or is generally overloaded.
15. Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical
It seems that there are duplicate pages for this topic. The copy you’re looking at is not canonical, and we believe Google has chosen a different page to be authentic. If you inspect Google’s search results, it will show what they have deemed as most accurate.
You must start working on your most valuable URLs (usually your ‘money’ pages) to bring your webpage up in search engine rankings. If these should not be indexed, add canonical URL tags and use meta robots tags or X-Robots-Tag HTTP headers. When Google indexes a page, they may show you their preferred URL version through their URL Inspection tool.
16. Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)
Googlebot is a bot that crawls the internet and indexes pages. It never provides credentials, so it should not be given an error for requesting them. This error should either be fixed, or the page should be blocked by robots.txt or noindex.
Make sure that Google has access to URLs you want your site to rank with. Applying noindex (in HTML or HTTP header) might be best if any other URLs are listed under this issue.
17. New Product Issues Detected for Site
The following warnings and Google Search Console errors directly relate to product-specific Structured Data Markup (SDM). Use the Structured Data Testing Tool to determine which elements are missing or set up incorrectly. Use schema.org and Google Search Console’s guide to understanding how structured data works for more information on how to fix these missing or incorrectly specified elements.
Either “Offers,” “Review,” or “aggregateRating” Should Be Specified:
- Cause: Product pages must have at least one of these elements specified within the SDM.
- Fixing these errors: Add at least one of these elements to the page or template HTML. These are typically parent elements with child elements underneath them, such as type, URL, ratingValue, or reviewCount.
Missing Field “Price”:
- Cause: This required product field should be entered as ##.##
- Fixing these errors: Ensure you include the price in the SDM in the format of “23.99” (no dollar sign should be present in this field.). When having the price field, be sure to also specify price currency in the offer markup. If you do not display prices on your website, do not include either of these fields.
Rating Is Missing, Required Best and/or Worst Values:
- Cause: If including product ratings or reviews, you must specify the range for “bestRating” and/or “worstRating” for each product.
- Fixing these errors: bestRating is typically 5 while worstRating generally is 1.
Value in Property “ratingCount” Must Be Positive:
- Cause: This property should contain the total number of ratings on the product page.
- Fixing these errors: While this can be 0 if there are no reviews on the product yet, this number can never be negative.
18. Google Search Console HTTPS Report
One of the key aspects of Google Search Console is the HTTPS report, which provides insights into how Google handles your website's use of HTTPS.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a secure version of HTTP that encrypts communication between a web server and a user's browser. This helps to protect user data from prying eyes and prevents man-in-the-middle attacks. Google strongly recommends using HTTPS for all websites, providing users a more secure and trustworthy experience.
What does the HTTPS report show?

The HTTPS report in GSC shows the number of indexed URLs on your website that use HTTPS vs. HTTP. It also provides information about any errors Google has encountered when crawling or indexing your HTTPS pages.
What to look for in the HTTPS report
The ideal scenario is for your website to have no HTTP URLs in the HTTPS report, indicating that all your URLs use HTTPS. However, if you see HTTP URLs listed in the report, try to fix the errors to provide a good page experience for your visitors.
Types of errors in the HTTPS report
- HTTPS crawling issue: This error occurs when Google cannot crawl or index the HTTPS version of a page. This could be due to various factors, such as a server configuration issue or a broken link.
- Other issues: This error occurs when there is an issue with the HTTPS version of a page that prevents it from being indexed, even though Google can crawl it. This could be due to a server-side error or a security vulnerability.
How to fix errors in the HTTPS report
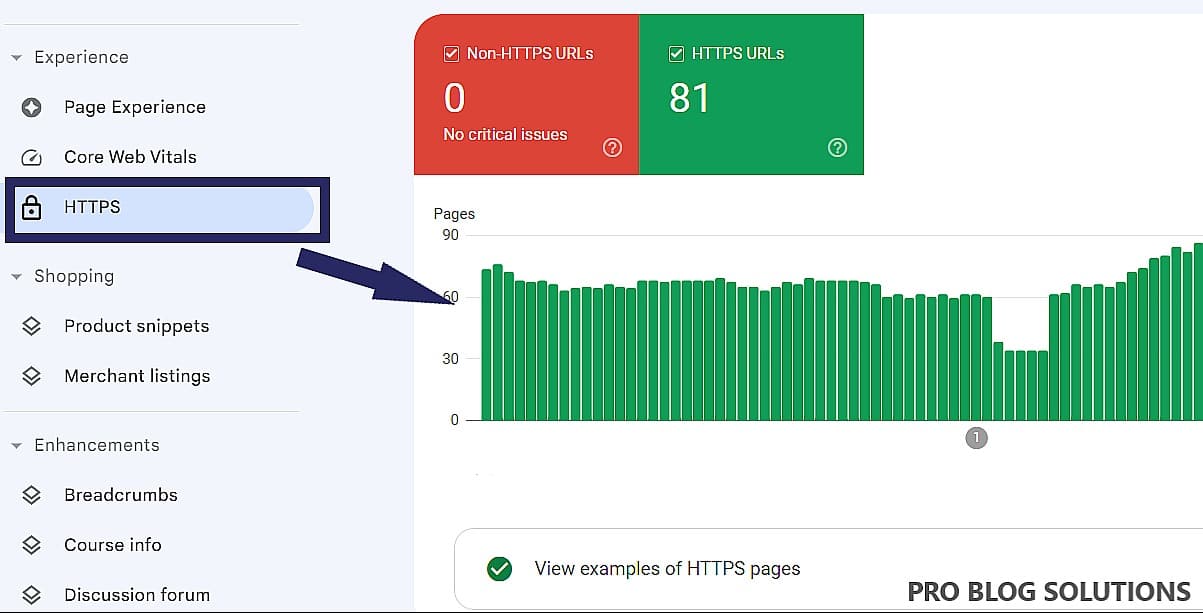
To fix errors in the HTTPS report, you will need to identify the root cause of the problem. Once you have identified the cause, you can take steps to resolve it. For example, if the error is due to a server configuration issue, you will need to contact your web hosting provider to get the problem fixed.
Benefits of using HTTPS
In addition to providing a more secure and trustworthy experience for users, there are other benefits to using HTTPS, such as:
- Increased search rankings: Google prefers websites that use HTTPS, which can lead to higher search rankings.
- Enhanced brand reputation: Using HTTPS can make your website look more professional and trustworthy, enhancing your brand reputation.
- Improved user experience: HTTPS can also improve the user experience by preventing mixed content errors and ensuring that your website loads securely.
How to switch to HTTPS
If you are not already using HTTPS for your website, you can switch to it by following these steps:
- Get an SSL certificate: An SSL certificate is required to enable HTTPS. You can purchase an SSL certificate from a variety of vendors.
- Install the SSL certificate on your server: Once you have purchased an SSL certificate, you will need to install it on your server. This will involve configuring your web server to use HTTPS.
- Redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS: After you have installed the SSL certificate, you must redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS. This can be done using various methods, such as server-side or browser-based redirects.
Fixing HTTPS Issues in GSC:
- Address issues other than HTTPS not evaluated first. Fixing other issues might fix these issues as well.
- For URLs with issues, click on the specific issue to see a list of affected pages. Generally, fixing the issues that affect the most pages is good.
- For each example error in the table, determine the HTTPS URL that was crawled for that URL: Search Console tests the HTTPS version of the HTTP URL.
- Follow the advice in the error description to fix the issue.
- Fix your HTTPS errors. If a site has a lot of HTTPS issues, it can prompt Google to stop crawling your HTTPS pages.
Using HTTPS is essential for providing a secure and trustworthy experience for your website's visitors. The HTTPS report in Google Search Console can help you identify and fix any issues with your HTTPS implementation, ensuring that your website is fully secure and optimized for search.
FAQs About How to Fix Google Search Console Errors in 2026:
-
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console is a free service offered by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site's presence in Google Search results.
-
What is the coverage issue in the Google Search Console?
The New Index Coverage Issue notices are part of Google's rollout of a new Search Console. It shows how well Google has indexed a site, showing changes over time. It also presents warnings about error URLs and indexing issues.
-
What is an HTTP 404 error in Google Search Console?
The HTTP error 404, more commonly called “404 error”, means that the page you are trying to open cannot be found on the server. This is a client-side incident, meaning the page has been deleted or moved.
Conclusion: Fix Google Search Console Errors in 2026
We have covered some common Google Search Console errors and their cause and fixed them in simple steps. With the help of tools, you can quickly resolve any Google search console errors. Identifying the errors becomes more straightforward and helps you improve the rankings.
Make sure your pages can be crawled and indexed by Google with no problem. While submitting a sitemap does not directly affect your rankings, it will help Google notify you of any errors that might negatively impact your website's rankings.





