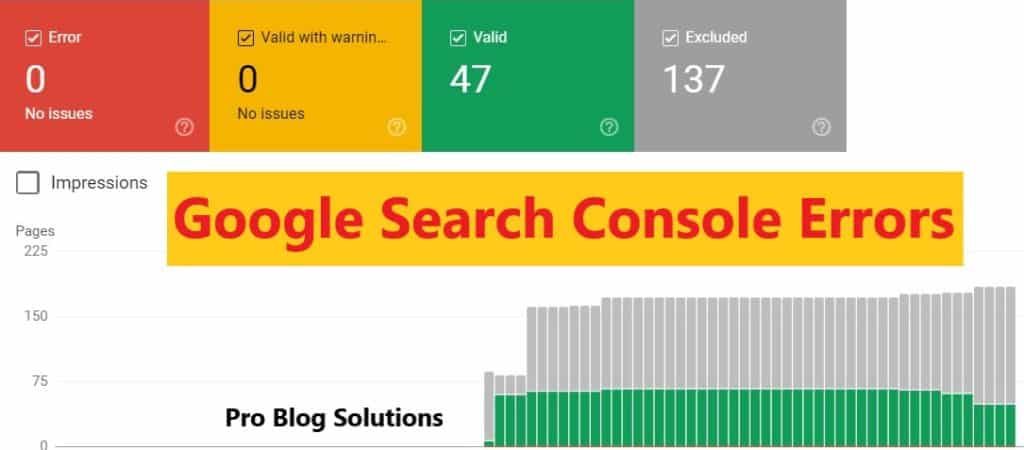
Google has released the Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console, which expresses the quality signals they use to improve User experience. So, how can we improve the core web vitals ranking factor? Let's understand in detail below.
Google has made numerous changes to its search algorithm to evaluate websites and rank them according to the quality, trustworthiness, and intent of the content it features.
In many cases, Google makes formal announcements before changing its algorithm. However, they also make several changes without announcing.
Along with the changes to its search algorithm, Google frequently changes its SERP ranking factors.
Webmasters have to develop innovative strategies with the changes in Google's algorithm. For such a strategy, they consider various ranking factors.
The latest ranking factor announcement from Google is the Core Web Vitals.
How can Google’s core web vitals affect the ranking of your website in Google search results? What changes do you need to make to your websites?
Finding answers to these questions has become necessary for website owners.
In this blog post, you will find a detailed guide to the different aspects of Google’s new ranking factor, Core Web Vitals.
What are Core Web Vitals?
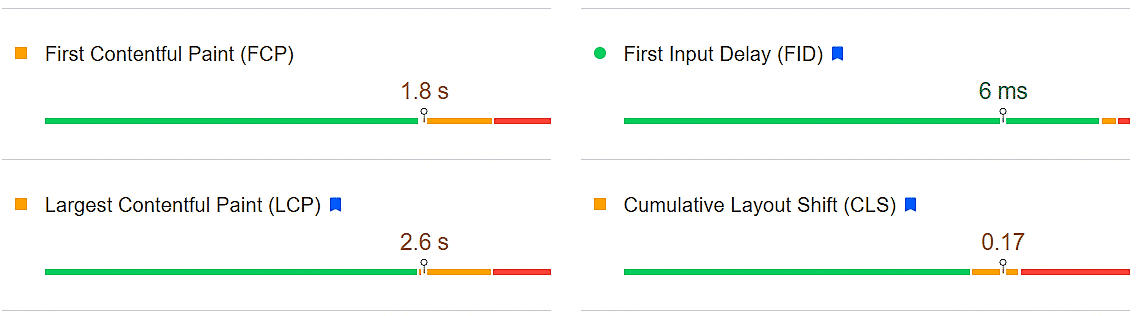
Core web vitals are essential for the page to provide a great user experience, focusing on loading, interactivity, and visual stability. Core Web Vitals is a collection of items that Google considers necessary for the overall web page user experience to improve core web vitals ranking factors.
Core Web Vitals are a subset of factors that will be part of Google’s page experience score.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals Ranking Factor
Page experience will be a mixture of factors that Google considers necessary for user experience, including:
1: Mobile-friendliness: Your page is optimized for mobile browsing.
2: Safe-browsing: Your page contains no malicious (malware) or misleading content (phishing).
3: HTTPS security: The page is served in HTTPS.
4: No intrusive interstitials: Your page should not have elements that obstruct your main content (such as a popup covering most of the content immediately after the user lands on your page).
Some websites that have good Core Web Vitals scores include:
- Google Search
- Wikipedia
- YouTube
- Amazon
These websites are all fast, responsive, and visually stable, which makes them a pleasure to use.
You may also like to read:
- Attract Readers to Your Blog With Easy Ways
- How to Protect Your Accounts From Online Phishing Scams?
- Easy Solutions to Increase Your Adsense Earnings
- Free Strategies to Drive Traffic to ECommerce Websites
- How to Make $100,000 With Google AdSense in 1 Year?
Core Web Vitals Basically Consists of 3 Facts
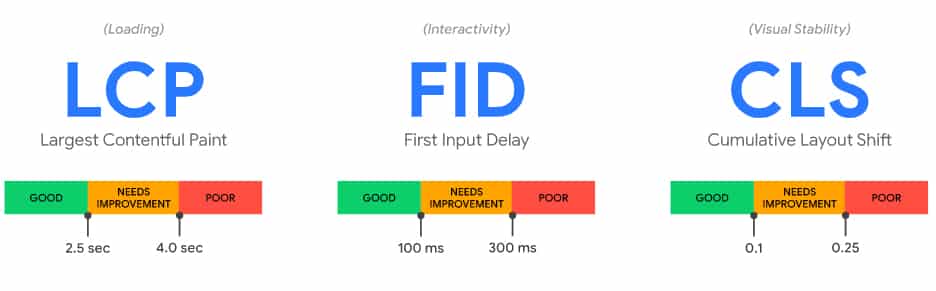
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – which measures the loading performance and should be less than 2.5 seconds.
First input delay (FID) – with measures interactivity should be less than 100 milliseconds.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures visual stability and should be less than 0.1.
Core Web Vitals are nothing new to webmasters. Still, Google announced its plan to update the algorithm under these elements, spurring a heightened urgency to optimize its core web vitals. This is true for digital marketing experts, but for newbies scratching their heads and wondering what Core Web Vitals are about, this brief guide is for you.
Core Web Vitals Report
Our site loads much faster now, and we have been trying to validate the fix report for a while.
It seems Google is reindexing the site based on these parameters, and we hope all of them will become “Good URLs. “
What Metrics do Core Web Vitals Consider?
These parameters can be implemented in many page speed testing tools like WebPageTest and Google PageSpeed.
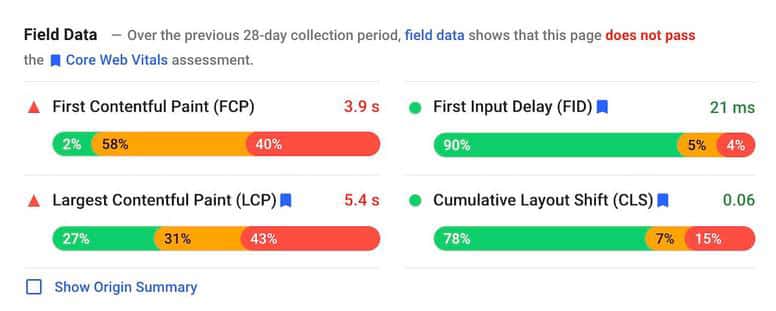
The quality of the on-page experience depends on several factors.
Core Web Vitals combines the main elements of a page-loading experience while the user accesses and interacts with its elements.
Now, let’s learn more about each Core Web Vitals metric.
How Important are Core Web Vitals for SEO?
Google says they will use improved core web vitals as page experience signals if several pages have equally great, relevant content.
So, optimizing the core vitals should not be prioritized over quality content, search intent, and page authority.
There are a few reasons why you should care about Core Web Vitals:
They impact your search ranking. Google has already announced that Core Web Vitals will be a factor in their search ranking algorithm. This means that websites with good Core Web Vitals scores will likely appear higher in search results.
They improve your user experience. Users are likelier to stay on your website and engage with your content if it loads quickly and is visually stable. This means that good Core Web Vitals scores can lead to increased website traffic and conversions.
They make your website more accessible. People with disabilities, such as slow internet connections or visual impairments, may be more likely to have a good experience on your website if it has good Core Web Vitals scores.
Quick Tips To Improve Your Core Web Vitals?
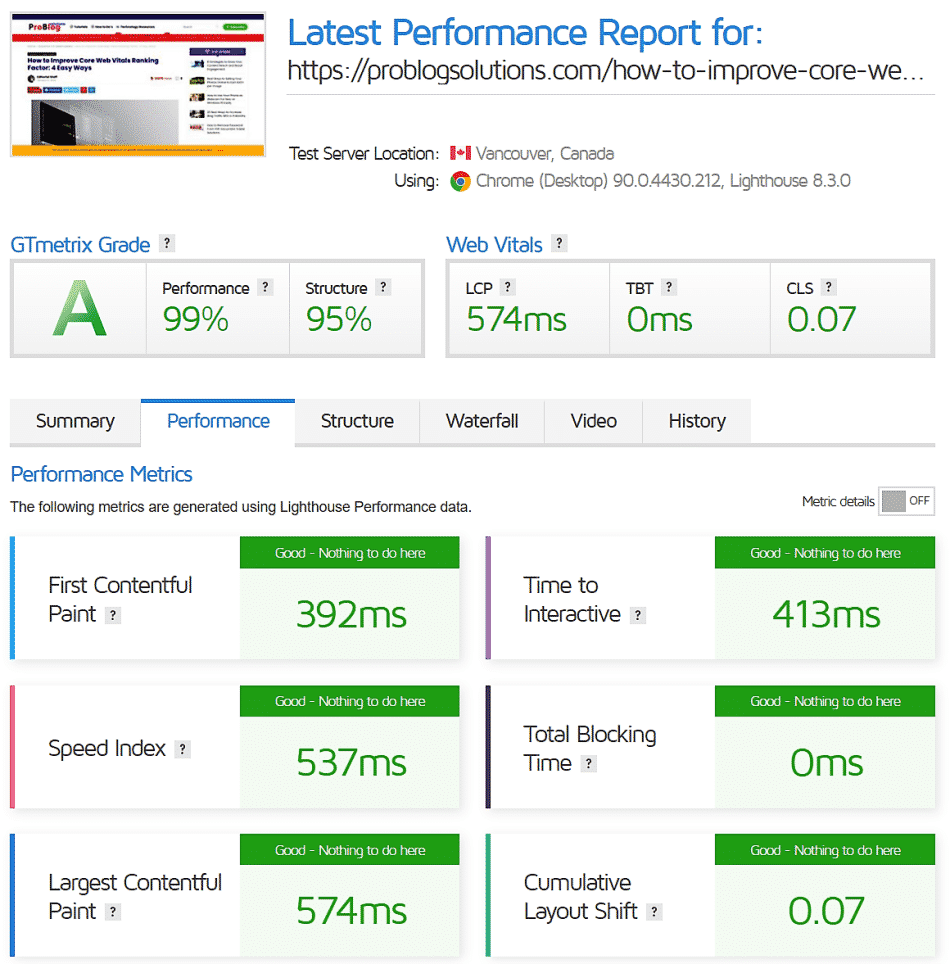
There are some things you can do to improve your Core Web Vitals scores:
- Optimize your images. Large images can take a long time to load, so optimizing them for the web is essential. This means using smaller file sizes and compressing them without sacrificing quality.
- Minify your code. Minimizing your code will remove unnecessary whitespace and comments, loading your pages faster.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN). A CDN will deliver your web pages from servers that are closer to your users, which can improve loading times.
- Test your website on different devices and browsers. Ensure your website loads quickly and looks good on various devices and browsers.
How to improve Core Web Vitals?
You can get to work now that you know within which metric gains can be made for your website.
In general, there are standard recommendations you can apply to score higher within the Core Web Vitals, but not all tips you find on the internet will help you.
There is much more to it, like what kind of device and internet connections your users have and where they come from.
But to get you well on your way to passing Core Web Vitals, we will discuss how you can start achieving better results.
Implement a Caching Solution
Caching is storing a copy of your files in a cache, temporary storage that may be accessed more quickly.
Enabling browser caching has many benefits because it can decrease server workload, boost load times, decrease latency, and consume less bandwidth.
The primary drawback is that at least two different versions of your website will always be available.
Running a real-time application that depends on accurate data can make this problematic. Still, even this can be partially fixed by forcing a subset of the cache to empty when new data is imported.
If you are using WordPress, here are some free plugin options:
Optimize All Media and Images
All websites and blogs have to display images. That’s a given, but so many high-quality images and videos can slow things down and considerably disadvantage you in ranking.
Your images must be optimized for mobile devices. This means setting them at a smaller width. You can do this with the help of plugins, such as ShortPixel Adaptive Images.
It’s also a brilliant idea to embed all your videos from a third-party platform, such as Vimeo or YouTube. This works as a better alternative to hosting them on your website.
Optimize JavaScript
One of the most significant factors in delayed reactions to user input is your site’s JavaScript files.
When the browser encounters a script in your website markup, it stops rendering its HTML by default until the script has been downloaded and executed.
Your first option to tackle this problem is to reduce unused JavaScript. Speed testing tools usually give you this warning with problematic files.
If you have a lot of redundant JavaScript code on your site, leave only the essential code snippets.
For the scripts on your website, control when they execute by using defer and async.
The defer attribute moves the JavaScript execution to the end of the loading queue, while async tells the browser to download it in the background and only execute it after that.
Here is an example of how to use them:
<script async src=”important.js”></script>
<script async src="important.js"></script>
<script defer src=”less-important.js”></script>
<script defer src="less-important.js"></script>
Implement Lazy Loading
We also recommend that you implement lazy loading.
This helps ensure that your images will load exactly when users get to that section of the web page rather than loading simultaneously as everything else on the page.
Lazy loading images can help improve your LCP and loading speed.
Many WordPress image optimization plugins like Smush have built-in lazy loading features.
Optimize Your Website Fonts
As with images, the fonts you use on your website can also influence loading times. This is because they require the browser to download and load the font family, including each variation of its weight combinations.
Optimizing your web fonts can help improve your website’s performance. This is because optimized web fonts are smaller in file size and delivered more quickly.
Also, a browser may not automatically render text elements if the associated web font hasn’t loaded yet. On the other hand, using fallback fonts may cause layout shifts, hurting your CLS score.
We recommend being selective in which fonts you use on your site. If you’re using more than two fonts, remove them from the specific elements and use global fonts to only apply the needed types and weights.
This will ensure that only the fonts you need for the text are downloaded.
Use a Content Delivery Network
A content delivery network (CDN) is a fantastic asset for reducing page load speed. It minimizes load lag time between your site’s server and your user’s browser by caching page information for future page loads.
While the difference between using and not using a CDN can seem minimal to most (often a few seconds), it can impact your load speed score immensely.
If you don’t have a CDN, when a customer loads your site, the page files are accessed from wherever your central server is hosting them.
The server stores those files through caching, preventing a browser from re-downloading everything on a page every time it’s visited.
But, if that server isn’t local, the loading time will lag. For example, if your customer is located in Florida and your server is in Europe, those files will take longer to load on your customer’s browser.
A CDN spreads your network out, reducing that lag time. Instead of just one server, your site can be loaded from dozens of different servers.
A user’s browser will load files from the server closest to them, and your page speed score will lift.
The CDN’s caching abilities also ensure a page’s assets are displayed faster the second time a consumer visits the site because the assets are already downloaded from the server and stored in the CDN.
If you don’t have a CDN, now’s the time to get one.
Ensure Fast Server Response Time
If it takes long to receive content from the server, the browser automatically delays rendering the same on the screen.
A slow server response time affects your website’s SEO and spoils the user’s experience. That may increase your bounce rate as well.
First, you need to check the current performance of your server by checking the following essential parameters,
- Check how fast the server is hosting your website.
- Check the CDN of your website.
- Check whether the usage of any specific plug-in is slowing the loading speed of your website.
After checking the above parameters, it is time to check the server response time using Time To First Bite (TTFB).
That will give you an idea of how long a user needs to wait to receive the first bite of your web page content after clicking.
Removing Useless CSS and JS
In your CSS and JS files, there are bits of code that are never used, and despite this, they are “read” entirely when your page loads. These data are loaded and processed unnecessarily.
The Chrome DevTools Coverage tab will help you understand the percentage of unnecessary code in your CSS or Javascript files.
Then, it will be necessary to check the code in each file and remove it if necessary.
Usually, a strategy consists of creating small chunks of JavaScript and CSS and loading them when needed.
You should remember that deferring files, loading files asynchronously, and cleaning up CSS and JS are pretty technical.
Improve Loading of Third-Party Scripts
For many sites, slowness also comes from outside. If your site relies on ad scripts, for instance, you are basically in the hands of the ad provider.
You can only hope that they make their ads performant. If their ads load slowly, maybe it’s time to find another provider.
If third-party scripts slow down your site, you should look into this. Ask yourself, do I need that particular ad? What’s the value of these scripts?
A different option might be more optimized and less stressful for your server. Maybe try that?
If possible, you can experiment with hosting the script yourself. This way, you’re more in control of the loading process. If you can’t do that, see if you can get it to preload quicker.
Tools to Track Core Web Vitals
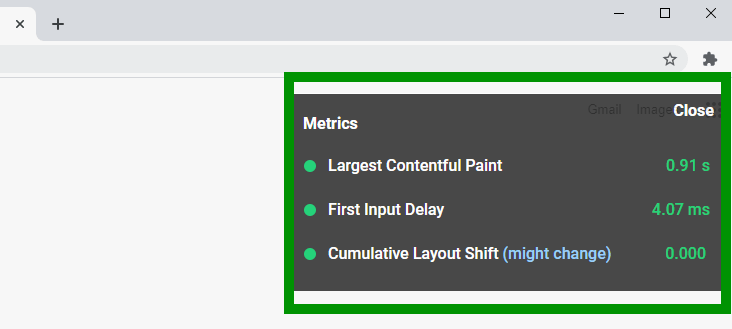
If you want to know how your website performs with Google’s Core Web Vitals and how to improve core web vitals, we have provided some valuable tools to help you get to grips with your website’s vital signs and give it a regular health check.
Lab Tools:
Field Tools:
- Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX)
- Search Console (Core Web Vitals report)
- web-vitals JavaScript library
Combined Tool:
- Google's PageSpeed Insights provides lab and field data about a page. It uses Lighthouse to analyze lab data, while real-world field data is based on Chrome's CrUX data.
Each can help you monitor your Core Web Vitals differently to improve core web vitals.
We suggest deep-diving into these tools to better understand how they can help you improve Core Web Vitals and boost your search engine rankings.
Improve Your LCP to Improve Core Web Vitals
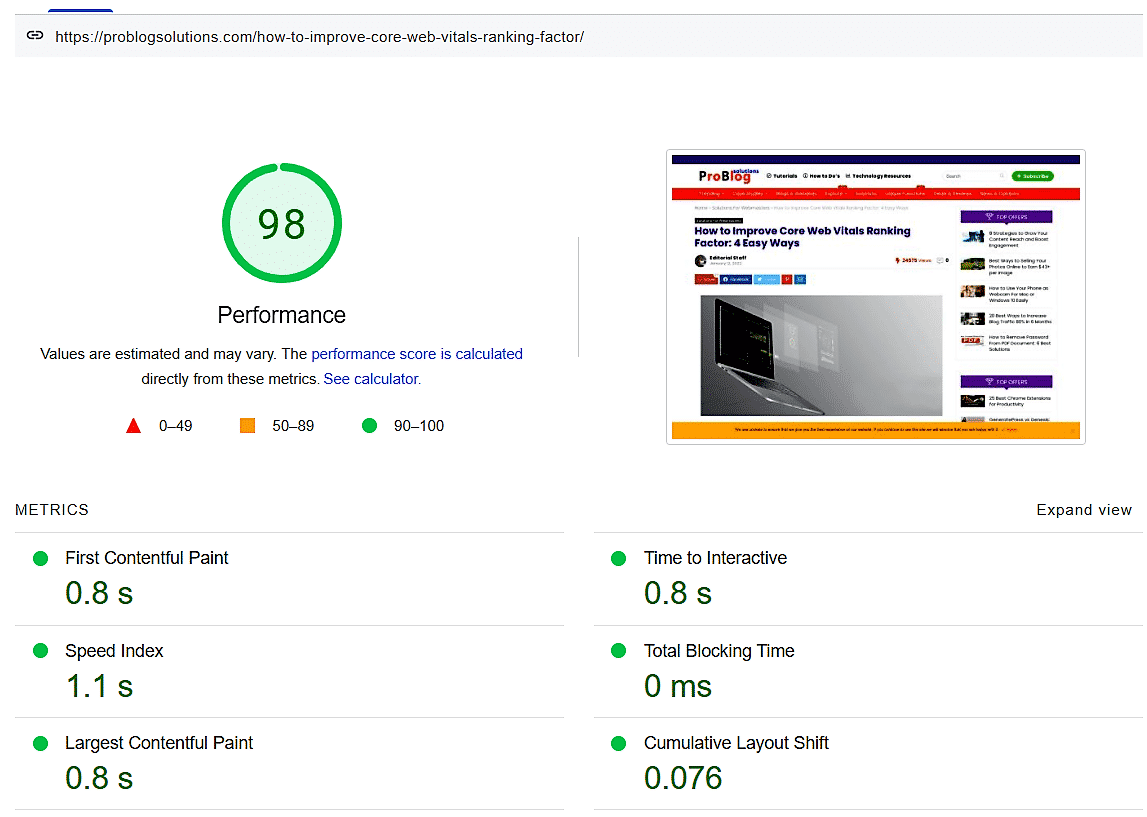
According to Google, these are the most common causes of bad LCP and suggestions on how to optimize them to improve core web vitals:
- Slow server response times
- Optimize your server
- Route users to a nearby CDN
- Cache assets
- Render-blocking CSS and JavaScript
- Minify CSS
- Inline critical CSS
- Minify and compress JavaScript files
- Minimize unused polyfills
- Slow resource load times
- Optimize and compress images
- Preload important resources
- Compress text files
- Client-side rendering
- Minimize critical JavaScript
- Use server-side rendering
- Use pre-rendering
Improve Your FID to Improve Core Web Vitals
To improve your First Input Delay, you can do the following to improve core web vitals:
- Break up Long Tasks
- Optimize your page for interaction readiness
- First-party script execution can delay interaction readiness.
- Third-party script execution can delay interaction latency.
- Use a web worker
- Reduce JavaScript execution time
- Defer unused JavaScript
- Minimize unused polyfills
Improve Your CLS to Improve Core Web Vitals
Improving the Cumulative Layout Shift can be achieved by optimizing the following causes of poor CLS to improve core web vitals:
- Images without dimensions
- Always include width and height size attributes on your images and videos.
- Each image should use the same aspect ratio.
- Ads, embeds, and iframes without dimensions
- Statically reserve space for the ad slot
- Take care when placing non-sticky ads near the top of the viewport.
- Eliminate shifts by reserving the largest possible size for the ad slot
- Choose the most likely size for the ad slot based on historical data.
- Dynamically injected content
- Avoid inserting new content above existing content.
- Reserve sufficient space in the viewport
- Web Fonts causing FOIT/FOUT
- Modify the rendering behaviour of custom fonts with
font-display. - The Font Loading API can reduce the time needed to get fonts.
- Use
<link rel=preload>on the critical web fonts.
- Modify the rendering behaviour of custom fonts with
More exciting articles for you:
- Successful Internet Marketing Tips for Your Business
- Best Website Builder Tools for Small Business
- How to Show Breadcrumbs in Google Search Results?
- Best Mobile Marketing Ideas to Enhance Your Business
- 89 High Domain Authority DoFollow Article Submission Sites
Audit Your Site for Security Issues
Along with mobile usage functionality, website security will also play a role in determining the page experience. Google is committed to ensuring that SERP websites are secure for users to view without the risk of security issues.
The main security issues to be aware of are malware, unwanted software, phishing, and deceptive content.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals Ranking Factor
An easy way to check whether or not your website has issues that could put your users at risk is to look at the Security issues report in Google Search Console.
This report can be found under the Security & Manual Actions heading.
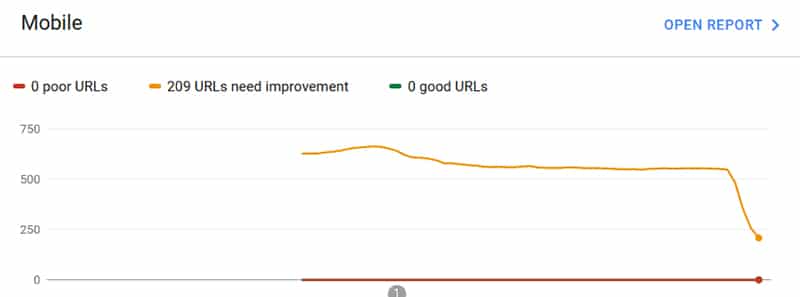
Clearly, it is early days, and it seems Google is indexing websites again based on these web vital parameters, and user experience will be a crucial factor now in SEO. Site speed has been a ranking factor for years, but this takes that to the next level. A simple page load time is not enough.
FAQs About How to Improve Core Web Vitals:
-
Does CLS affect SEO?
CLS score will affect your SEO. While it's likely a minor factor, your CLS score (along with the other Web Vitals) may reflect the traffic you get from search engines.
-
What is Web Vital?
Web Vitals is an algorithm from Google to see how they measure your site for one of their crucial website quality indicators.
-
What is the largest Contentful paint?
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) is a Core Web Vitals metric and measures when the viewport's largest content element becomes visible. It determines when the page's main content has finished rendering on the screen.
Final Words on Improve Core Web Vitals Ranking Factor:
When it comes to search engine rankings, user experience becomes more critical.
While high-quality content and a well-thought-out SEO plan should remain one of your top priorities, you must think carefully about user experience and how you can improve core web vitals ranking factors.
Google puts site speed and user experience first and foremost. We’ve always looked at SEO as a priority.
Although the tips mentioned above can help you improve Core Web Vitals ranking factor scores, you should do this to offer your visitors a better user experience.
Have you checked your website's Core Web Vitals? What are your reports suggesting? Feel free to comment below. We will be happy to assist you further.