Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the world, and the field of cyber security is no exception. AI-powered tools are already being used to detect and prevent cyber threats, and this trend will continue, but what do you think about how AI can provide unrivalled protection against emerging AI-driven cyber threats.
As artificial intelligence is becoming more and more common in our society, it’s also gaining ground in the cybersecurity sector for good and evil. As we leverage the latest AI-powered tools to strengthen our cybersecurity, cybercriminals also utilize the same technologies to develop more sophisticated attacks and break our defenses.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that focuses on creating intelligent machines that can work and think like humans. It involves designing algorithms, computer programs, and systems that can analyze data, learn from it, and make decisions based on that learning. AI technology is used in various applications, including robotics, natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning.
AI systems are designed to mimic human intelligence, which includes the ability to reason, learn, perceive, understand natural language, and make decisions. AI techniques such as deep learning, neural networks, and natural language processing are used to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and learn from experience. AI aims to create machines that can think, reason, and make decisions in a way that is similar to human beings.
There are two main types of AI: narrow or weak AI and general or strong AI. Narrow AI is designed to perform specific tasks, such as image or speech recognition, while general AI is designed to perform any intellectual task a human can do. General AI is still in the early stages of development and is not yet available.
AI is used in many applications, including self-driving cars, voice assistants, fraud detection, and virtual assistants. It can transform many industries, from healthcare to finance to manufacturing, by automating repetitive tasks, improving efficiency, and enabling new forms of innovation.
However, AI also raises ethical and societal concerns, such as the impact on employment and the potential for bias in decision-making. As AI advances, it is essential to consider the ethical implications and ensure its benefits are shared fairly and equitably.
There are several reasons why AI is so well-suited for cyber security. First, AI is very good at pattern recognition. This means that AI-powered tools can quickly identify malicious patterns in data, such as those found in malware or phishing emails.
Second, AI can learn and adapt over time. AI-powered tools can better detect threats as cybercriminals develop new attack methods.
In addition to these general advantages, AI has several specific cybersecurity benefits. For example, AI can be used to:
AI-powered cybersecurity tools will likely become even more powerful and effective as AI develops. This will be essential in the fight against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
How AI Can Improve Cyber Resilience?

Here are some ways AI can improve cyber resilience:
- Identifying threats: AI can analyze large amounts of data to identify potential threats. This can be done by looking for behaviour patterns indicative of malicious activity. AI can also identify new threats that have not been seen before.
- Mitigating threats: Once a threat has been identified, AI can be used to minimize the impact of the threat. This can be done by blocking the threat from reaching its target or minimising the damage it can cause.
- Responding to incidents: AI can also respond to cyber incidents. This can be done by automatically detecting and responding to attacks or by providing assistance to human analysts who are responding to incidents.
AI can play a significant role in improving cyber resilience. By automating threat detection and response, AI can help organizations identify and mitigate threats more quickly and effectively. This can help to reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Here are some specific examples of how AI is being used to improve cyber resilience:
- IBM Security QRadar Advisor with Watson: This AI-powered security solution uses machine learning to identify potential threats and provide recommendations for remediation.
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR: This AI-powered security platform provides a unified view of threats across the entire attack surface, making identifying and responding to attacks easier.
- Cisco Tetration Analytics: This AI-powered security solution uses machine learning to identify and respond to real-time threats.
These are just a few examples of how AI is being used to improve cyber resilience. As AI technology develops, we expect to see even more innovative ways to use AI to protect our data and systems from cyber threats.
In addition to the above, here are some other ways AI can be used to improve cyber resilience:
- AI-powered anomaly detection: AI can identify anomalies in network traffic or user behaviour that may indicate malicious activity.
- AI-powered threat intelligence: AI can collect and analyze threat intelligence from various sources to identify emerging threats and develop mitigation strategies.
- AI-powered incident response: AI can automate incident response tasks, such as identifying and containing threats and notifying affected users.
By using AI to automate and improve various aspects of cyber security, organizations can significantly improve their cyber resilience and reduce their risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
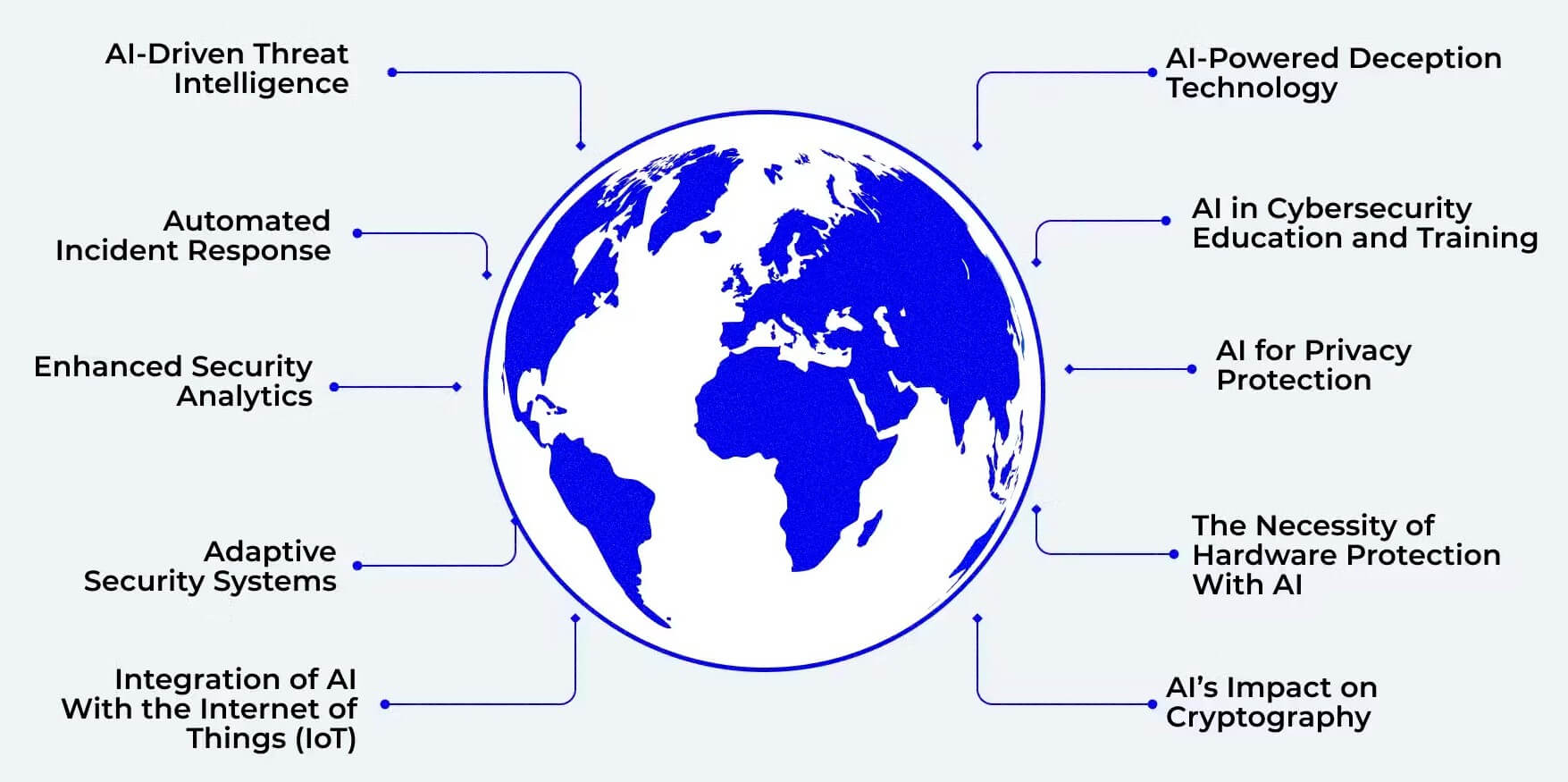
How AI is Being Used to Protect Against Emerging AI-Driven Cyber Threats:
There are several ways that AI is being used to protect against emerging AI-driven cyber threats. Some of the most common methods include:
1: Machine Learning
Machine learning is used to develop new algorithms to identify and block malicious traffic. Machine learning algorithms can be trained on large datasets of known malware and phishing attacks. This allows them to learn to recognize new threats as they emerge.
2: Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing analyses text-based threats, such as phishing emails. Natural language processing algorithms can identify keywords and phrases often used in phishing emails. This allows them to flag these emails for further review by human analysts.
3: Computer Vision
Computer vision analyses images and videos for signs of malicious activity. Computer vision algorithms can identify objects and patterns often associated with malware or phishing attacks. This allows them to flag these images and videos for further review by human analysts.
Benefits of Using AI in Cybersecurity
AI can be used to improve cybersecurity in several ways, including:
- Detecting threats: AI can analyze large amounts of data to detect potential threats, even those unknown to security experts.
- Responding to threats: AI can be used to automate the response to security threats, which can help to speed up the time it takes to mitigate an attack.
- Preventing threats: AI can identify and mitigate vulnerabilities in software and systems, which can help prevent attacks from happening in the first place.
In addition to these benefits, AI can help improve cybersecurity teams' efficiency and effectiveness. By automating tasks and identifying threats more quickly, AI can free up security professionals to focus on more strategic and critical work.
AI is a powerful tool that can be used to improve cybersecurity. As AI technology develops, we will likely see even more innovative ways to use AI to protect our systems and data from attack.
Limitations of Using AI in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used in cybersecurity to help organizations detect and prevent cyberattacks. However, there are several limitations to using AI in this context.
One limitation is that AI-based systems can be expensive to develop and deploy. Additionally, AI systems require large amounts of data to train and maintain, which can challenge organizations with limited resources.
Another limitation is that AI systems can be susceptible to false positives. This means that the system may incorrectly identify the benign activity as malicious, leading to disruptions in business operations and loss of productivity.
Finally, AI systems can be biased, meaning they may be more likely to identify specific types of activity as malicious than others. This can lead to discrimination against certain groups of people or organizations.
Despite these limitations, AI has the potential to be a powerful tool for cybersecurity. By carefully considering the limitations of AI and taking steps to mitigate them, organizations can use AI to improve their security posture and protect themselves from cyberattacks.
Here are some of the specific limitations of AI in cybersecurity:
Despite these limitations, AI has the potential to be a powerful tool for cybersecurity. By carefully considering the limitations of AI and taking steps to mitigate them, organizations can use AI to improve their security posture and protect themselves from cyberattacks.
What is the Future of AI in Cybersecurity?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the cybersecurity landscape. AI-powered tools are already being used to detect and respond to threats, and their capabilities will only grow.
One of the most promising applications of AI in cybersecurity is threat detection. AI can analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns indicating a potential attack. This can be done much faster and more accurately than by human analysts.
AI can also be used to respond to threats. Once a threat has been detected, AI can automatically deploy countermeasures to protect the system. This can help to prevent or mitigate the damage caused by an attack.
In addition to threat detection and response, AI can be used for various other cybersecurity tasks. For example, AI can be used to:
- Identify and classify malware.
- Analyze network traffic.
- Monitor user behaviour.
- Generate security reports.
As AI technology develops, its role in cybersecurity will only grow. AI-powered tools will become more powerful and sophisticated and can handle more complex tasks. This will help organizations to improve their security posture and protect themselves from increasingly sophisticated threats.
FAQs: How AI Provides Unrivalled Protection Against Emerging AI-Driven Cyber Threats
-
Why is AI So Important to Cyber Security?
AI is crucial for cybersecurity due to the increasing complexity and volume of cyber threats. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data, detect patterns, and identify threats in real time. This allows organizations to respond more quickly and effectively to cyber attacks, reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
-
Can AI for Cyber Security Replace Cyber Security Professionals?
AI can only partially replace cybersecurity professionals, as human expertise is still needed for complex decision-making and handling novel threats. However, AI can complement human efforts by automating repetitive tasks, allowing experts to focus on high-priority issues and strategic planning. This collaboration between AI and cybersecurity professionals creates a more robust and effective defense against cyber threats.
-
Why Is AI Adoption So Widespread and Rapid in the Cybersecurity Field?
The rapid adoption of AI in cybersecurity is driven by the need to address the growing number of cyber threats and the shortage of skilled security professionals. AI helps automate routine tasks, accelerates threat detection, and enhances decision-making processes, making it an invaluable tool for organizations to strengthen their security posture.
Who Benefits More from AI’s Role in Cybersecurity: The Good or The Bad Guys?
While both sides benefit from AI’s role in cybersecurity, it can’t be denied that AI has immense potential for making the online world more secure.
As AI continues to evolve, it is clear that it will play an increasingly important role in cyber security. AI-powered tools can potentially revolutionize how we protect our systems and data from cyberattacks.
AI can help us discover and prioritize risks, direct incident response, and detect cyber threats before damage is done. Although AI has drawbacks, such software is critical in strengthening cybersecurity. But our role is to ensure that AI's rise doesn’t get out of control.






